Raw data is collected from various channels and stored in databases, but in order to make it useful, it has to be processed to be displayed. The first step is Data Reporting. It involves using various tools to define and store data, while professionals monitor trends, the process of data collection, and the performance of the enterprise.
Thus, data reporting is the process of collecting, storing, and displaying data to monitor the performance of a process. It requires certain skills and tools.
Data Reporting and data analytics, though often used interchangeably, are two different processes, but analytics is dependent on data reports. Here is the complete guide to understanding data reporting solutions and services.
Table of Contents
- Definition of data reporting
- What are data reports
- What is the purpose of data reports
- What is the importance of data reporting
- Here’s how to write a data report
- Reporting versus analytics – what’s the difference?
What is Data Reporting?
Data Reporting can be defined as the process of collecting, storing, and displaying data to monitor the performance of a process. It can help engineers, marketers, managers, or other professionals monitor the performance of their processes.
Data Reporting is also a type of service where a company collects data from a variety of sources and then sends it to clients or other companies for further action.
Such data reports can then be used to determine trends in the performance of processes by monitoring the data over time. That is data analysis.
The analytics provides answers to questions like, “What improvements need to be made in your product sales process”, or, “Why are our costs changing? Why are we losing/gaining business?”
Data analysis is defined as the process of analyzing data collected by a data reporting system. Data analysis helps improve the process of data reporting. Reports should raise questions about the business from their end-users. But data reports do not have context, they simply present the facts.
By interpreting the data at a deeper level and providing actionable recommendations, the analysis seeks to answer questions.
This comprehensive guide will help you understand data and data reporting, and its use. You’ll learn what information is collected, how it is collected, how it’s used, and the skills required, among other things.
Achieve business success with our data analytics consulting services
Data Reporting Basics
What are data reports, how do they work, and what are the common types of data reports? Here are some answers:
Basics include:
What is a data set?
A data set is made up of the data that you want to capture and present. These are the actual source documents that contain the data that you are interested in.
The following are common data sets that are used for data reporting:
Financial and operational data: Data that is provided by an organization’s accounting system or other financial and operational systems such as enterprise resource planning (ERP) software.
You can extract financial and operational data from the source documents and bring it into a data mart before sending it to a reporting server for reporting.
Customer relationship management (CRM) data: Data from various systems that can be extracted from source documents to a data mart.
For example, you can extract customer information from a CRM system and put the data into a data mart for reporting.
Archival data: Data that was captured in source documents. If you need the same data several times, extract it from the source documents and load it into a data mart before sending it to a reporting server for reporting to save time and effort.
What are Data Reports and the Types of Data Reports?
Data reporting is the process of creating digestible data by translating raw data into formats that help you assess the success of your organization.
There are several different kinds of data reports. They can be classified by the kind of information they report on and the manner in which they do so.
When it comes to presenting your data, there are two different types of reports: static and interactive. Static reports are simple to create and understand but do not allow users to interact with them. Most pull data from a single source, hence are called static.
Static reports provide “historical” data, i.e. of events that have already occurred. Eg: What was the cost per lead acquisition?
Interactive reports also called real-time or dynamic reports, provide access to data as it is collected in real-time. Because they update data continuously, they allow users to drill down into the data to uncover a deeper meaning.
What types of reports do you typically create? The primary type of report is a list, which provides a brief view of the facts from source documents without presenting them in a context that can then be used down the line to make decisions.
For example, you can create a list of key facts, key dates, or key costs. An example would be: How many customers opened bank accounts, in which months, last year?
What Data are You Reporting?
The next step in designing reports is to determine the information you want your users to view and the results you want them to get.
A report is a detailed presentation of facts and can come in summary form, too. Then, there’s the query. Data Report summaries provide a snapshot of an organization’s performance.
They are usually generated for top management, who then disseminate the information to their staff.
Form queries are more complex. They are typically requested by users to filter the information they want.
For example, an analyst might want to look at sales growth by individual products, geographical locations, or customers within particular organizations.
They may want to know how many customers opened their accounts in the previous year. So they ‘query” the database for the answers.
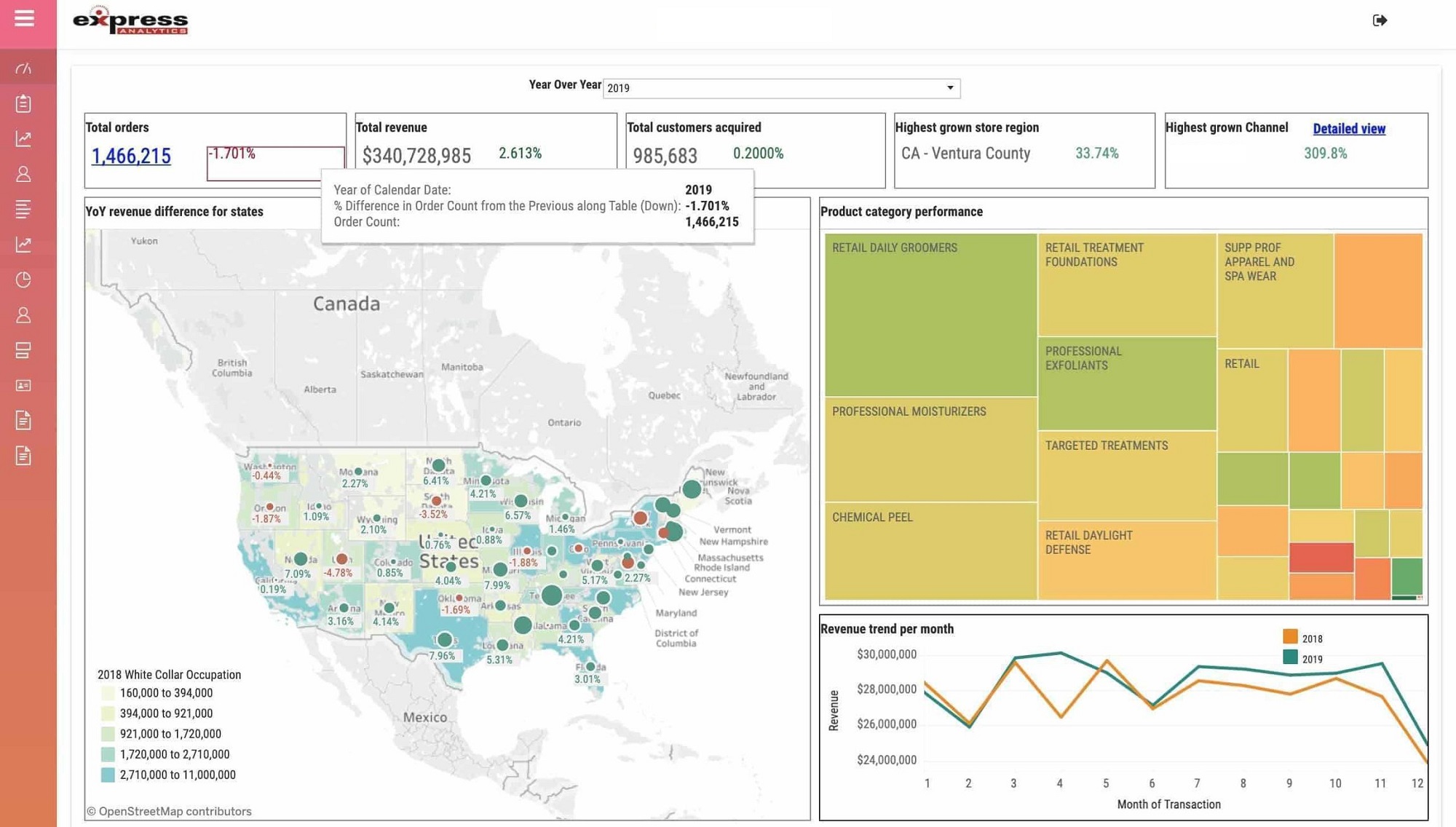
What is the Purpose of Data Reports?
- To present information to analysts and managers so they can make effective business decisions
- To present information to analysts and managers so they can improve the performance of their organization
- To improve the quality of existing information
- For managers, it is to satisfy information needs so they can make informed decisions
How do you format it?
- Each column is a separate information item or entity
- Each line of a report summarizes a specific set of information
- If a set of information items is too large to fit on one page, it is broken into sections or lines
- A report usually contains several sections: title, purpose, list of information items, and organization chart
- The sections should be labeled, described, and described in detail
Data Reporting Tools
A data reporting tool performs the actual data reporting by collecting data from within your business processes.
The data reporting tool collects data from the business processes being conducted by the company. The data reporting tool can be an Excel spreadsheet or some other type of electronic reporting tool.
The Importance of Data Reporting
Here’s why should you care about data reporting.
If data is not reported, there are two reasons why:
1) the data was not measured or
2) the data was measured but not reported
Not measuring is never an option, but reporting is often optional. If the data is not reported, it does not exist, in a sense. The data can’t be used for making decisions. This can be a problem.
Also, not all data should be reported to make a decision. If a person is making a decision based on certain assumptions, they need the actual data to see if it supports the assumptions.
Why Measure the Data?
There are many reasons you would want to measure data, but there are five main ones:
1) it helps to mark the stages/progress of a business
2) it helps understand what is going on with competitors
3) it is a valuable measurement tool for taking action
4) it helps you improve your data management process
How to Write A Data Report?
These are the basic components of a good data report:
1) title and introduction
2) business logic
3) data summary
4) group by and sort criteria
5) visualizations
6) drill down
7) conclusions and recommendations
8) references and appendices
9) footnotes and credits
A good data report should include all of these elements, but it doesn’t need to be perfect.
The main points to remember when writing a data report are:
1) make sure your report isn’t too long
2) Define the type of data report you are trying to create
This includes the purpose and objective of the report. Data should be presented in a way that allows decision-makers to make an informed and confident decision based on your data and analysis.
3) Make sure to explain the purpose of the report
The data report should be designed in a way that helps the user answer the following questions:
1) What is the data in this report?
2) What conclusions can be drawn from this data?
3) What actions should take place because of this information?
The target audience should be able to clearly define the key issue being addressed by the report. This is very important.
What are Data Reporting Skills?
Many organizations simply store raw data from various sources within Excel, Access, SQL Server, MongoDB, NoSQL database, etc. But to prepare a data report, you need the following skills:
- Ability to compile a list of all the data that you have from research or other sources
- Identify important data and use it
- Compile a list of reports for end-users
- Present these reports to end-users in different formats
Achieve business success with our data analytics consulting services
Report Vs. Analytics: Know the Difference
If you’re considering using the data to make the decision about what should happen next, should report or analytics be your guide?
A data report is a process of compiling data. It can be as simple as having a list of activities. But to take it a step further, the report has to be analyzed to deliver a statistical measure of a company, individual, product, or service.
The analysis uses data to answer strategic business questions, while a report uses data to track the business’ performance.
Think of a story as a presentation to an audience. Storytelling allows you to use the actual data and show the inner workings of your data model or analysis in such a way that people can understand what they’re seeing and why it matters.
Here’s an explanation by QuestionPro:
Reporting: The process of organizing data into informational summaries in order to monitor how different areas of a business are performing.
Analysis: The process of exploring data and reports in order to extract meaningful insights, which can be used to better understand and improve business performance.
So data analytics is a mathematical representation of the data and models that can also be used to describe how to predict what will happen in the future. Think of analytics as a set of formulas; it’s what you use to predict the results.
Understanding the difference between a Report and Analytics could be one of the most important things to do if you’re looking to build meaningful insights from your data.
Reports will usually be much more ‘raw’, meaning they’re not quantified, and they don’t include any data analysis. They’re a way of getting your data out there so you can look at it and understand what’s going on.
If you just wanted to see the number of new visitors that have come to your site, then you’d use a report. So, reports generally include facts and statistics about a particular topic or event, but because there’s no quantifying, it’s not likely that the information will be very meaningful.
Analytics, on the other hand, will almost always include some kind of analysis of the data that you’ve collected.
It may be that the only insight that they’ll provide is what proportion of visitors are returning or how much time people spend on your site.
Or maybe you want to find out how many visitors are coming from specific countries or what type of device they’re using to view your site.
So clearly, the difference is in what they provide. In data-driven decision-making, analytics is often referred to as the “visualization part”.
What makes one a reporting tool and the other an analytics solution? The report is usually printed out in PDF format, sent to the user by email or Excel, or uploaded to a website.
The reports are usually visually oriented, but not generally specific enough to be useful in the decision-making process.
On the other hand, an analytics solution provides a specific set of tools to help users make better decisions.
Often this means it has a graphical user interface (GUI) which allows a user to click a few buttons and have graphs and charts appear on the screen. Other times it means that the analytics are embedded within another system.
The data provided by the analytics tool is used to identify trends, spikes, anomalies, and anomalies (e.g., outliers). If you’re not familiar with statistics then this might be an area that’s beyond your capabilities.
In conclusion: To make raw data useful, it has to be processed and displayed. Data is collected from various sources and stored in databases, but it must be processed to extract value. Data reporting, not to be confused with data analytics, involves the use of various tools for defining and storing data, along with the monitoring of trends, the collection process, and overall performance.
Therefore, data reporting refers to the process of collecting, storing, and displaying data to monitor a process’ performance. The process requires a certain level of skill and a certain set of tools. Reporting and analytics are distinct processes, despite often being used interchangeably.
An Engine That Drives Customer Intelligence
Oyster is not just a customer data platform (CDP). It is the world’s first customer insights platform (CIP). Why? At its core is your customer. Oyster CDP is a “data unifying software.”
Liked This Article?
Gain more insights, case studies, information on our product, customer data platform


No comments yet.